Project 6
Automation Reliability and Dual-task Performance
Automated decision aids are used in various fields, such as military operations and medical diagnosis. To ensure appropriate trust and reliance on these systems, our study focuses on the following research question:
- How do different types of likelihood information impact human operators’ trust in automation and their team performance?
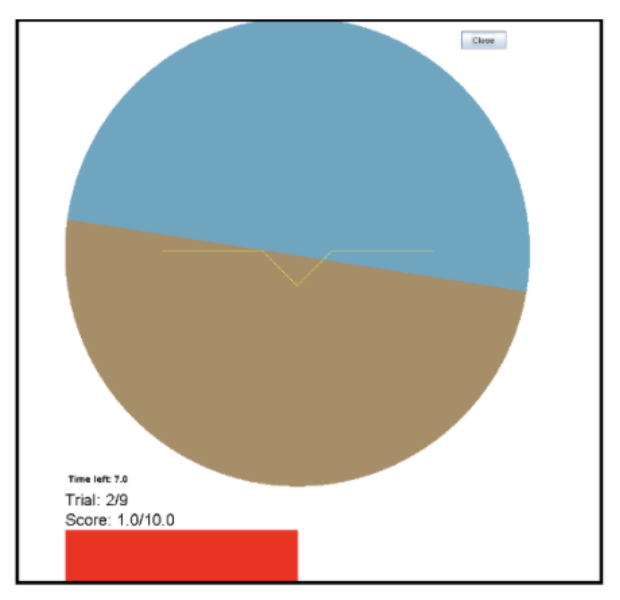
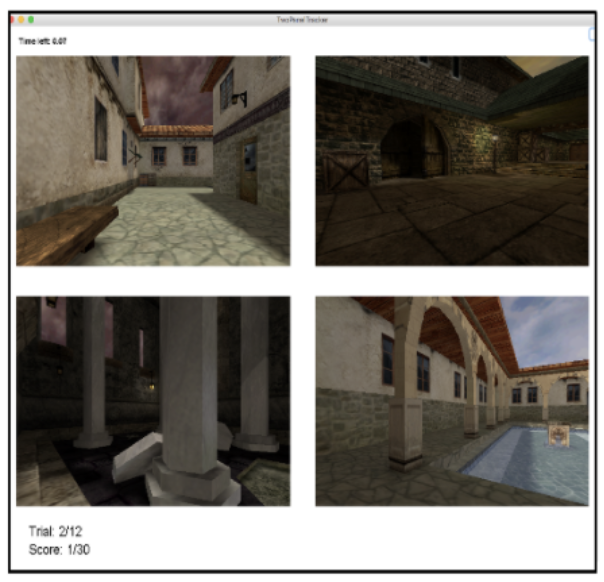
Dual-task environment in the simulation testbed.
To investigate this, we designed and conducted an experiment in the context of a simulated surveillance task. The results indicate that not all likelihood information equally aids human-automation team performance. Specifically, automated decision aids should avoid directly presenting the hit and correct rejection rates. These findings can be applied to the design of automated decision aids to improve human-automation team performance.
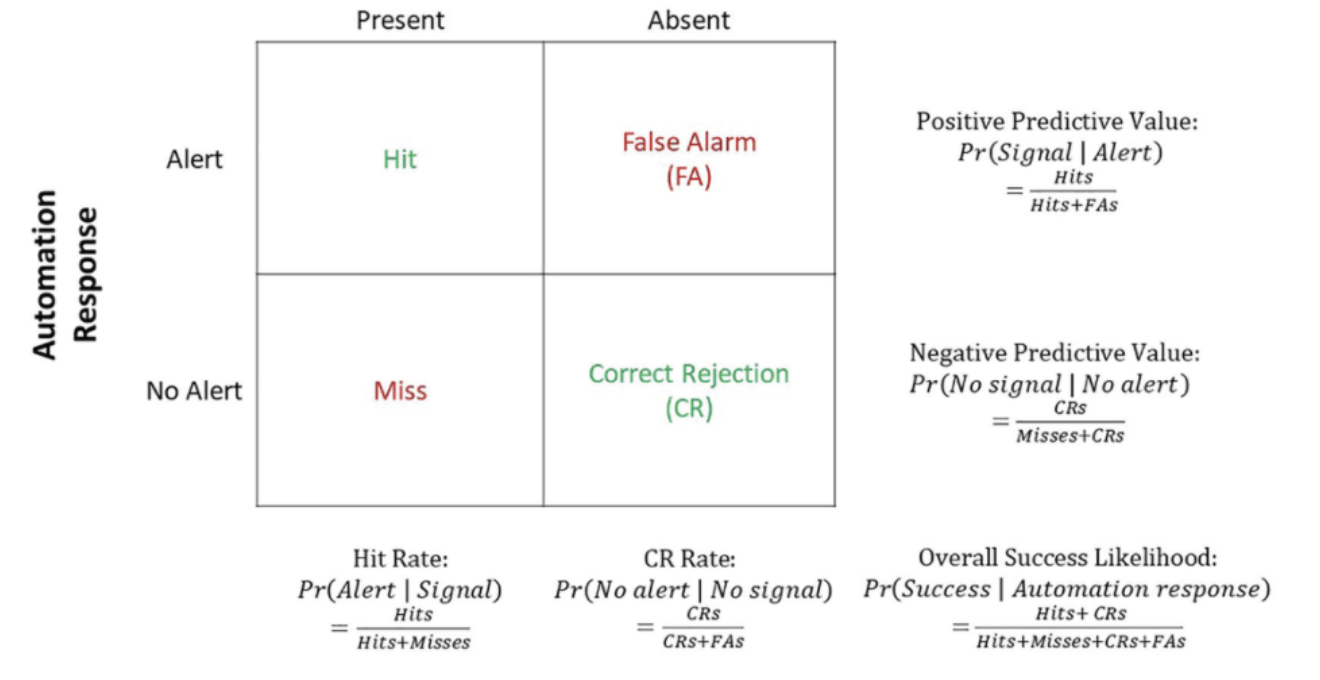
Signal Detection Theory (SDT) and Calculations of Hit Rate, CR Rate, Positive Predictive Value, Negative Predictive Value and Overall Success Likelihood.
Publication
- Du, N., Zhang, Q., & Yang, X. J. (2018, September). Evaluating effects of automation reliability and reliability information on trust, dependence and dual-task performance. In Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting (Vol. 62, No. 1, pp. 174-174). Sage CA: Los Angeles, CA: SAGE Publications.